The growing reliance on technology has transformed the way we travel, with mobile booking apps becoming an essential tool for modern-day tourists. However, this convenience comes at a price, as cyberattacks targeting travel booking apps have become increasingly prevalent. These attacks not only pose a threat to the security and privacy of users but also have a significant impact on the tourism industry as a whole.
Consequences of cyber attacks on travel booking apps
With the advent of mobile apps, travelers can easily book flights, accommodations, and tours at their fingertips. This convenience has revolutionized the way people plan and experience their trips. However, as the popularity of these apps has grown, so has the interest of cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities.
The impact of these attacks extends beyond the individual users; it can lead to significant financial losses for travel companies – according to data published by IBM in the „Annual Cost of Data Breach” report, the average cost of a data breach in 2022 for the travel industry was USD 2.94 million.
Common types of cyber attacks on travel booking apps and real-life examples from recent years
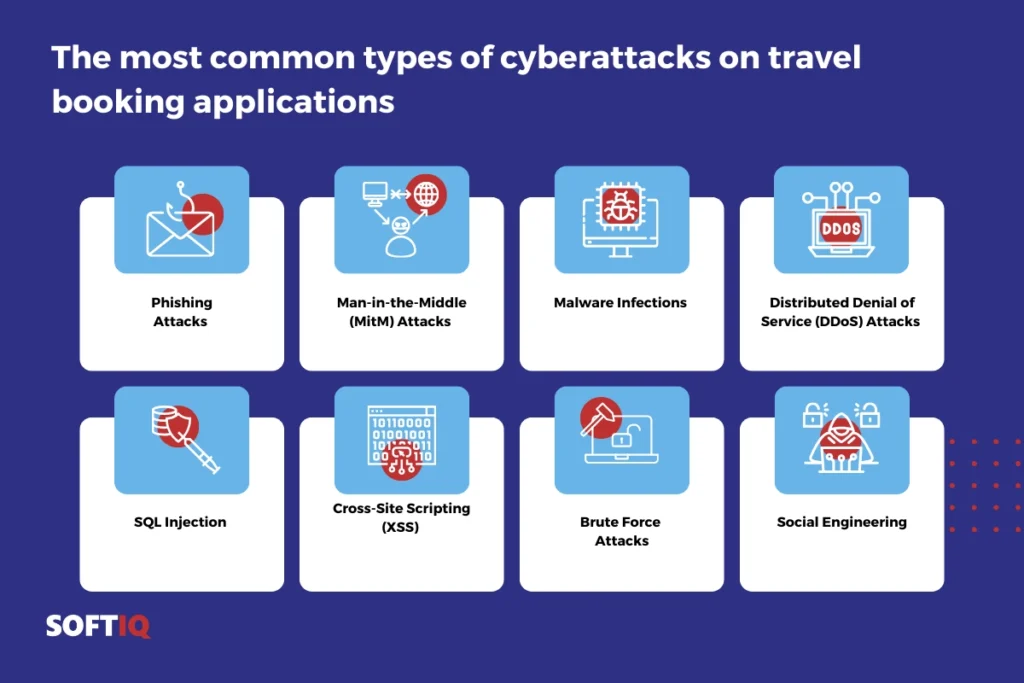
1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks involve tricking users into revealing their personal information or login credentials by posing as a legitimate entity. Cybercriminals often send deceptive emails or messages that appear to be from trusted travel booking apps, asking users to provide sensitive information such as passwords or credit card details. Once obtained, this information can be used for identity theft or financial fraud.
One notable example of such an attack dates back to 2020 when customers of one of the biggest online booking providers were targeted. Cybercriminals sent out phishing emails claiming to offer special discounts or promotions to customers. These emails contained malicious links that redirected users to fake websites resembling official platform. Once on these fraudulent sites, users were prompted to enter their login credentials and payment details, which were then harvested by the attackers.
While specific figures are not publicly available, thousands of individuals likely fell victim to this scam. The stolen information could be used for various malicious purposes, including unauthorized access to user accounts and financial fraud.
2. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
In MitM attacks, cybercriminals intercept communication between a user and a travel booking app’s server. By eavesdropping on the communication channel, attackers can gain access to sensitive data transmitted between the user and the app, including login credentials and payment information. This type of attack is particularly dangerous when users connect to public Wi-Fi networks that are not secure.
According to cybersecurity experts, one of the biggest attacks of this type affected approximately 380,000 customers of a large British airline in 2018. The attackers employed a Man-in-the-Middle attack to intercept and steal sensitive information, including names, addresses, and payment card details. This incident not only highlighted the potential consequences of MitM attacks on travel booking apps, but most of all, resulted in financial losses for both, the affected customers and the airline itself.
3. Malware Infections
Malware refers to malicious software that is designed to disrupt or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. Travel booking apps can be targeted by malware infections through various means, such as downloading infected files or clicking on malicious links. Once installed on a user’s device, malware can steal sensitive data, log keystrokes, or even take control of the device.
In 2018 a popular travel booking app) was hit by a malware attack that exposed sensitive information of its users. The attack was caused by a third-party vendor’s code that was embedded in booking software. The malware was able to steal users’ login credentials, travel itineraries, and credit card information. It is estimated that over 300,000 users were affected by the attack.
4. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
Such attacks aim to overwhelm a travel booking app’s servers with a flood of traffic, rendering them inaccessible to legitimate users. By exploiting vulnerabilities in the app’s infrastructure, cybercriminals can launch massive DDoS attacks that disrupt services and cause significant financial losses for the targeted app.
One of the most significant attacks of this type on an online travel agency was reported back in 2015 when the company was forced to take its websites and mobile apps offline. The attack, which lasted for several days, affected millions of users and caused significant delays and cancellations.
5. SQL Injection
With this attack type, hackers target the underlying databases of travel booking apps. By injecting malicious SQL code into user input fields, attackers can manipulate database queries and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information stored within the app’s database. This can include personal user data, payment details, or even administrative credentials.
In 2014 one of the largest online travel booking platforms experienced a significant data breach due to a SQL injection attack. The attackers exploited a vulnerability in the website’s search feature, injecting malicious SQL code into the search parameters. This allowed them to bypass authentication mechanisms and gain unauthorized access to the company’s customer database.
As a result of this attack, the personal information of approximately 800,000 customers was compromised. The stolen data included names, addresses, email addresses, and partial credit card information. The company promptly notified affected customers and took measures to enhance their security systems to prevent future incidents.
6. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Such attacks involve injecting malicious scripts into web pages viewed by users of a travel booking app. These scripts can be used to steal sensitive information, such as session cookies or login credentials, from unsuspecting users. XSS vulnerabilities can arise from improper input validation or inadequate security measures implemented by the app’s developers.
There are no publicly disclosed data breaches in travel booking apps, caused by this type of attacks, but risk of using XSS by cybercriminals is high and such vulnerabilities are frequently discovered by security researchers.
For example, in 2020, a security researcher identified an XSS vulnerability in one of the largest online travel booking platforms website that allowed attackers to inject malicious code into hotel reviews. While the exact number of affected users was not disclosed, this vulnerability could potentially impact a significant number of platform users who read or submitted hotel reviews. The injected code could be used to perform various malicious actions, such as redirecting users to phishing websites or stealing their personal information.
7. Brute Force Attacks
Brute force attacks involve systematically trying all possible combinations of passwords until the correct one is found. Cybercriminals may employ automated tools to launch these attacks against travel booking apps, attempting to gain unauthorized access to user accounts or administrative panels. Weak or easily guessable passwords are particularly susceptible to brute-force attacks.
In 2018 one of the largest airlines in North America experienced a brute force attack on its mobile app. The attackers used a botnet to try a large number of login credentials in an attempt to gain access to the app’s systems. Although the airline claimed that no sensitive information was stolen, the attack caused significant disruptions to its mobile app services.
8. Social Engineering
This type of technique exploits human psychology to deceive users into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. Attackers may impersonate customer support representatives, tricking users into providing their login credentials or other personal information. Social engineering attacks often rely on psychological manipulation rather than technical vulnerabilities.
One of the most known examples of such an attack was reported in 2019 when one of the world’s largest online travel booking platforms, experienced a data breach due to a social engineering attack. The attackers posed as company employees and contacted customer service representatives, convincing them to provide login credentials to gain unauthorized access to customer accounts. This breach potentially exposed personal information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses of an undisclosed number of users. While the exact number of affected users was not disclosed publicly, it is estimated that millions of customers were potentially impacted.
Preventing cyber attacks on mobile booking apps
In the face of growing cyber threats, travel companies must implement effective preventive measures to protect their mobile booking apps and their users.
Collaborating with cybersecurity professionals and software houses, such as SOFTIQ helps to ensure that all software and systems are up to date with the latest security patches.
Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing can help identify and address any potential weaknesses before they can be exploited by cybercriminals.
Additionally, implementing strong authentication protocols, such as two-factor authentication, can add an extra layer of security and make it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access. Educating users about common cyber threats, such as phishing attacks, and promoting good security practices, including strong passwords and regular password changes, can also go a long way in preventing successful attacks.







